
Last update: 26/01/2023
Are you familiar with the legislation regarding the use of audio protection, which types are available, and how you can best maintain them? Do you know how to care for earmuffs, earplugs or otoplastics and ensure they last as long as possible?
This guide will teach you all you need to know about audio protection and which device(s) you need in your company, when they must be worn and much more.
- Why should you wear audio protection?
- When should audio protection be worn (limits and health supervision)?
- Decibel values
- Norms and marking
- Attenuation levels
- What types of audio protection are there?
- Life expectancy and maintenance
Why wear audio protection?
In many companies, workers have to contend with noise on a daily basis. This includes noisy machinery, tools such as chainsaws, loud production processes or transport methods.
Too much noise can lead to problems such as hearing loss and tinnitus, and even to mental health issues.
Noise also affects the ability to concentrate, productivity falls and people are more likely to make errors.
When should audio protection be worn?
Audio protection is governed by European Directive 2003/10/EC, which indicates when audio protection must be worn.
The law works on the basis of three limits for daily exposure to noise: 80, 85 and 87 decibels (dB).

Lowest action value: 80 dB
Do workers have to deal with noise levels over 80 dB or peaks of 135 dB? Then audio protection must be provided. Employees must be trained on the risks of noise and be given instructions on the correct use of the audio protection devices.
Upper action value: 85 dB
When noise levels reach 85 dB or higher, or peaks of 137 dB, employees must wear audio protection. Long-term exposure to these levels will lead to hearing damage.
As an employer, you must train employees and provide them with information on the risks, take measures to reduce the risks, and cordon off dangerous zones.
Limit: 87 dB
The legal maximum limit is 87 dB or peak levels of 140 dB: employees must not work with noise that exceeds this level. You must immediately identify the cause, take measures to reduce the noise level and also take preventive measures.
Period of exposure
To prevent hearing damage, employees must not work for too long in noisy environments.
At 80 dB, this is a maximum of 8 hours per day, at 83 dB it is 4 hours and at 86 dB it is just 2 hours. You may only work with noise levels of 89 dB for half an hour and at a level of 95 dB for 15 minutes.
Health supervision
During the mandatory health audits, the Committee for prevention and protection at work (CPBW) will assess the risks, the measures taken to reduce the noise risks, and the selected audio protection.
At 80 to 85 dB or peak levels of 135 dB, these take place once every 5 years. Is the average from 85 to 87 dB or are there peaks of 137 dB? Then the health audit will take place every 3 years.
Are employees exposed to an average of 87 dB or peaks of 140 dB every day? Then there will be an annual check.
As a reminder...
| Limit value | Measures | Health supervision |
|---|---|---|
| 80 dB(A) |
|
Every 5 years |
| 85 dB(A) |
|
Every 3 years |
| 87 dB(A) |
|
Every year |
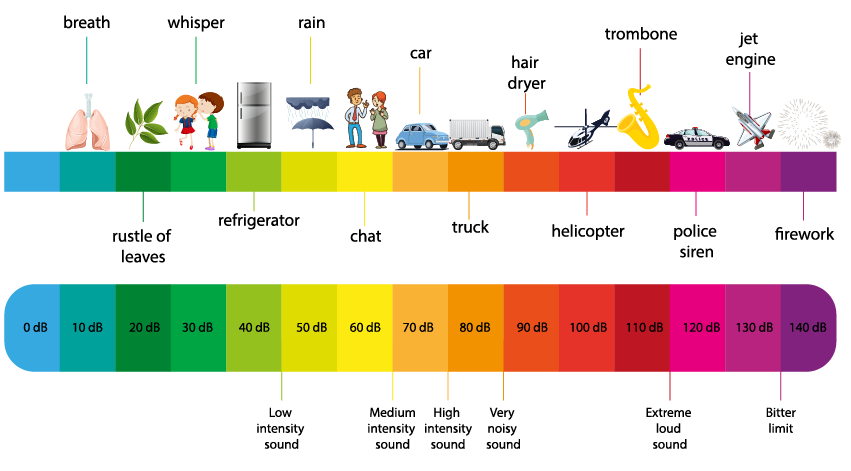
Decibel values
How loud is 80 dB?
The noise level of a quiet conversation or street is around 40 dB. An ordinary conversation is around 60 dB and a busy motorway is about 80 dB. The noise level of live music is about 90 dB. Our pain threshold lies at 120 dB.
Norms and marking
According to the European Directive, audio protection must comply with the EN 352 norm.
This includes information, definitions, and testing methods, and covers the effectiveness of audio protection equipment. Every audio protection device has its own code:
- EN 352- 1: earplugs
- EN 352- 2: earmuffs
- EN 352- 3: earmuffs attached to an industrial safety helmet
- EN 352- 4: level-dependent earmuffs
- EN 352- 5: active earmuffs
- EN 352- 6: earmuffs with electrical audio input
- EN 352- 7: level-dependent earplugs
There is no marking on earplugs This can be found on the smallest packaging component (bag or box).
Marking is highly brand-dependent on reusable earplugs and otoplastics.
Some brands use colours to indicate the type of filter and/or which audio protection unit goes in the left or right ear.
Some elements are indicated consistently for earmuffs, i.e.
- Brand name and company logo
- Article name
- CE seal of approval
- The EN standard (EN 352)

Attenuation levels
Audio protection devices have an attenuation level that indicates by how many decibels the noise is reduced on average.
This can help when choosing the right type of audio protection.
There are 3 ways to indicate this value:
SNR value (Single Number Rating)
The SNR value is one average attenuation value for all frequencies.
An SNR value of 35 dB, for example, indicates that a noise level of 100 dB would be reduced to 65 dB.
This figure is a good way of comparing different audio protection devices.
In most circumstances, machines make noise within specific frequencies. To make a final choice, we recommend working on the basis of the HML values and frequencies.
HML value (high, medium and low frequencies)
The HML value determines the frequencies (high, medium and low) in all three groups of frequency, and is thus more accurate than SNR values.
- H = between 2000 and 8000 Hz
- M = between 1000 and 2000 Hz
- L = between 63 and 1000 Hz
Octave band analysis
This is the most accurate method, because octave band analysis measures the noise level at even more frequencies (63, 125, 250, 500, 1000, 2000, 4000 and 8000 Hz).
SNR, HML and octave bands are all found on the packaging.

What types of audio protection are there?
There are various devices for protecting your ears against noise, with different properties and options. The most well-known are earplugs, banded earplugs, earmuffs and otoplastics.
Your choice depends on your working environment and what they will be used for.
| Hearing protection | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Disposable earplugs |
|
|
| Reusable earplugs and banded earplugs |
|
|
| Passive earmuffs |
|
|
| Active noise-reduction earmuffs |
|
|
| Communication earmuffs |
|
|
| Otoplastics - audio protection |
|
|
Disposable earplugs
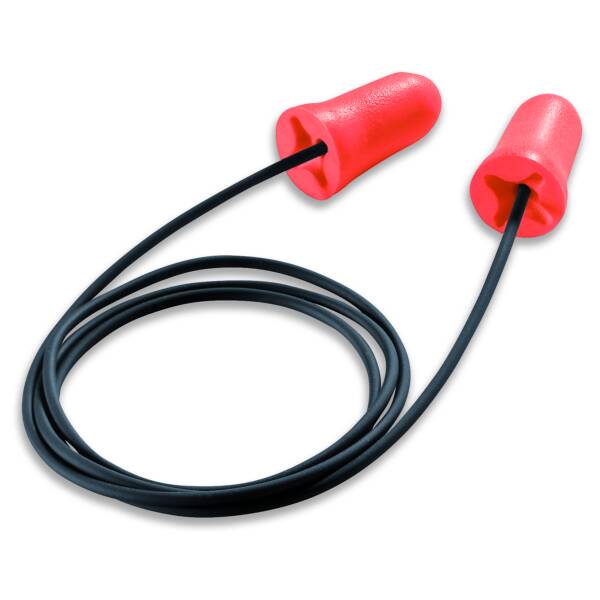

These earplugs are made of foam and adapt to the ear canal. They feel light and are available in various attenuation levels, with or without a cord, can be supplied via a dispenser and can be detectable (or not).
Unless they are used with a cord, they are not suitable for hygienic environments (food or pharmaceutical industries).
The disadvantage of (disposable) earplugs is that they create pressure in the ear and get dirty quickly. You must also ensure that they are inserted correctly in order to achieve the desired attenuation level.
Reusable ear plugs
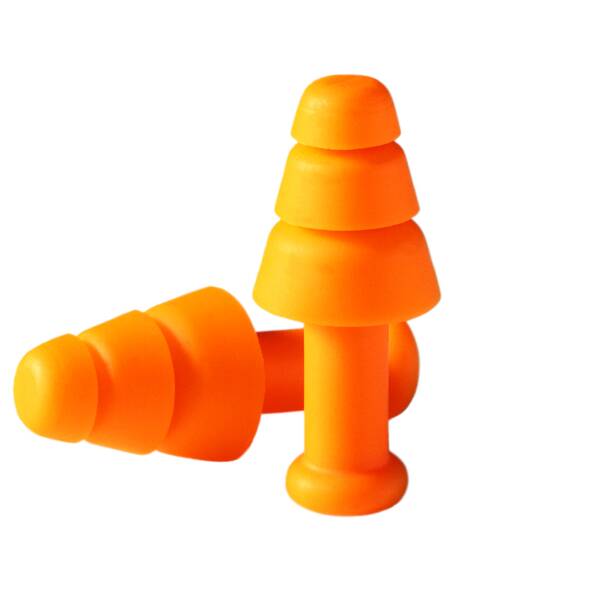

Reusable earplugs are pre-formed. They are easy to clean. They can be kept hygienic and are ideal for the food or pharmaceutical industry.
Reusable earplugs are more environmentally-friendly than disposable earplugs.
Banded earplugs
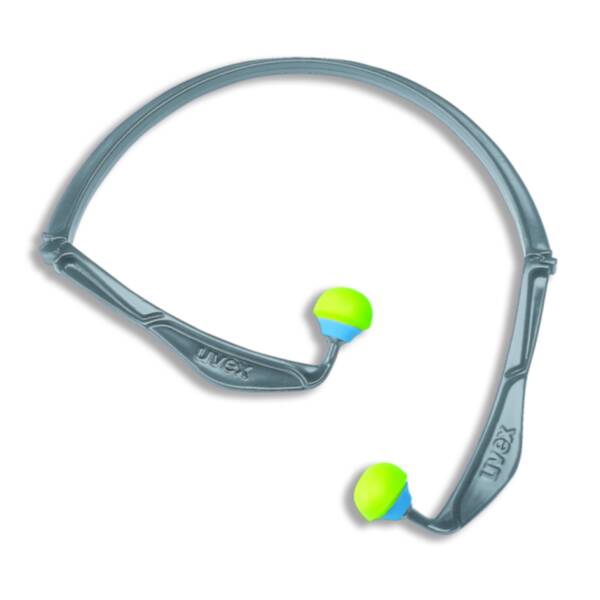

Do you need audio protection for a short period or just every now and then? Then banded earplugs are a good choice.
You always have them to hand, but have both hands free. They are also cheaper than earmuffs.
Earmuffs
Earmuffs can be passive or active.
Passive earmuffs
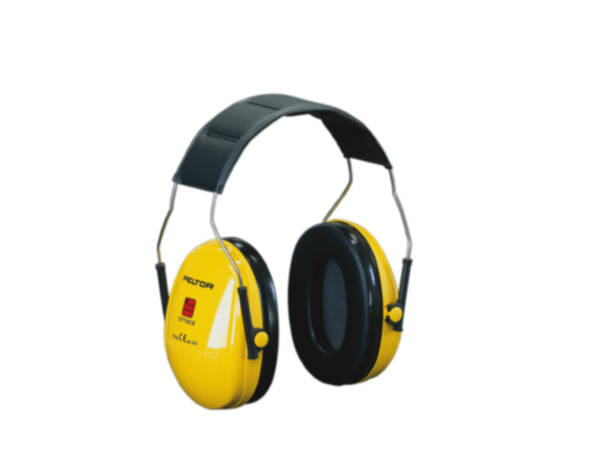

Passive earmuffs work without electronics. They attenuate the noise due to their construction and the materials used.
They are primarily suitable for high impulse noise, such as alarm signals, but are less suitable for continuous noise.
In the long term, earmuffs are more cost-effective than earplugs. As a result of being easy to use, they always offer the correct attenuation value.
Active noise-reduction earmuffs
Active noise-reduction earmuffs work with electronics. They detect the noise outside the earmuffs via a microphone and amplify and transmit this via a speaker in the earmuffs. As a result, you can communicate and hear alarm noises.
Active earmuffs can also offer 'active noise cancelling’. Ambient noise that is received by the microphone is then converted into a signal with the opposite phase.
These earmuffs are suitable for low acoustic pressure levels and low frequencies. They are also ideal for routine work, such as production line tasks.
As a result of the electronics, they are more expensive and feel heavier than passive earmuffs or earplugs.
Earmuffs with radio and/or Bluetooth
These earmuffs attenuate ambient noise, but the wearer can also listen to the radio. Nowadays, many earmuffs use DAB+, which uses digital sound quality.
Earmuffs with Bluetooth can be connected to your smartphone and you can then call and communicate with this device.
See all earmuffs with Bluetooth
Communication earmuffs
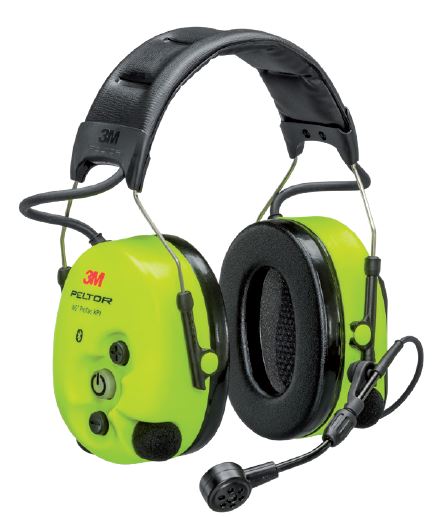

These earmuffs have a walkie-talkie function and are operated electronically.
As a result, you can talk to one another in noise areas, but still maintain your distance. Super safe, especially with COVID-19!
See all communication earmuffs
Helmet earmuffs
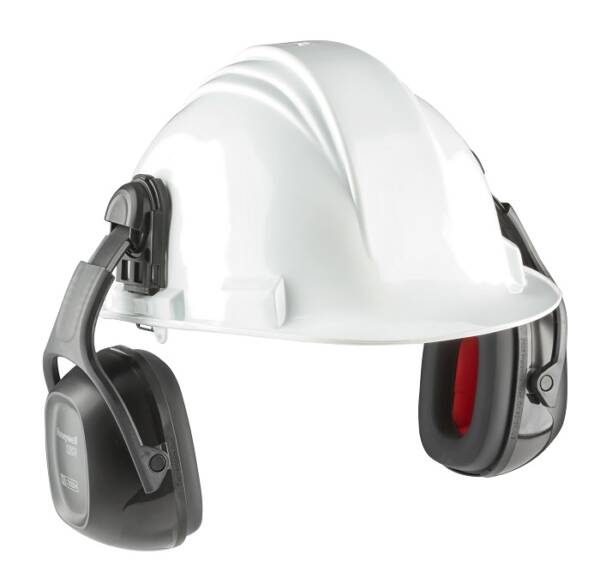

Helmet-mounted earmuffs are easily attached to an industrial safety helmet This usually involves an adapter but varies per brand.
They are available as passive, active or communication earmuffs.
See all helmet-mounted earmuffs
Otoplastics - audio protection

Otoplastics are earplugs that are tailor-made according to a print of your ear canal. They are extremely comfortable as a result.
You can also use filters which ensure the correct noise attenuation in a specific working environment. They also enable effective communication with other people.
In most cases, the level of acceptance among employees is very high when you have selected otoplastics.
Furthermore, you pay a fixed price per user. So, you know what your costs will be.
Find out more about Otoplastics
Life expectancy and maintenance
Earplugs
Earplugs generally last for one shift. Disposable earplugs must be replaced more frequently than reusable earplugs. Once you have used them, they do not need maintaining and are disposed of in the rubbish bin.
Reusable earplugs and banded earplugs are cleaned with warm water and soap or a disinfectant cleaning product. Then dry with a soft cloth.
Earmuffs
Earmuffs last somewhat longer. Change the ear cushions regularly so that the attenuation level remains consistent. Most brands provide hygiene sets so that you can replace them regularly. We recommend you do so twice per year.
If you use communication earmuffs, don't forget to replace the microphone too.
Otoplastics - audio protection
Want to use comfortable audio protection in the long term? Then choose otoplastics. Thanks to their personalised character, and an annual leak test, they offer comfortable ear protection for a considerable time.
Just like earplugs, you can clean otoplastics with soap and water. Or use the cleaning product and cloth supplied.
